If you want to work with private modules hosted on GitHub and still have all the advantages of GitHub Actions, you will have to jump through a handful of hoops first. This post is mostly a reminder for myself so that I don’t forget half of the step again and again and wonder why access doesn’t work.
So, let’s imagine you have Go application named github.com/zerok/go-private-application hosted in a private repository on GitHub. This application depends on the code in another private repository: github.com/zerok/go-private-library. Your user has access to both, but you also want to have CI working using GitHub Actions.
Initially, the workflow for the application would look like this:
name: Go
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v3
with:
go-version: 1.19
- name: Build
run: go build -v ./...
- name: Test
run: go test -v ./...
That’s pretty much what the Go template gives you on GitHub. Note that the build job won’t work simply because it will not be able to access the private library.
go: downloading github.com/zerok/go-private-library v0.0.0-20221118070615-c6a3ea2486af
Error: main.go:6:2: github.com/zerok/go-private-library@v0.0.0-20221118070615-c6a3ea2486af: invalid version: git ls-remote -q origin in /home/runner/go/pkg/mod/cache/vcs/b84cd954bd5fcf956bfa9c97858e9703e7dab951cdaa10412070739dd271d67f: exit status 128:
fatal: could not read Username for '[https://github.com](https://github.com)': terminal prompts disabled
Confirm the import path was entered correctly.
If this is a private repository, see [https://golang.org/doc/faq#git_https](https://golang.org/doc/faq#git_https) for additional information.
Error: Process completed with exit code 1.
GONOSUMDB
First, you should prevent the Go tool from looking up your private dependencies in the global sum database. This can be done by setting the GONOSUMDB environment variable:
# ...
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
GONOSUMDB: "*github.com/zerok/go-private-*"
# ...
SSH all the things!
Next, Go will try to fetch data via HTTPS. GitHub doesn’t offer something like project-scoped API keys, though, and so you’ll need to go with using SSH for all interactions with the library repository. Git itself can be configured to help here by automatically resolving certain URLs to different addresses, which is what the following step in the job is for:
# ...
steps:
# ...
# Now enforce that GitHub dependencies are fetched via SSH
- name: Enforce SSH
run: |
echo "[url \"ssh://git@github.com/\"]" > ~/.gitconfig
echo " insteadOf = https://github.com/" >> ~/.gitconfig
# ...
This should be executed before the build or test steps.
Key management
Finally, the library project must know that the application CI should be able to access it. For this, create an SSH key-pair for the application and then add the public key to the go-private-library project.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f go-private-app.key
This will create two files:
go-private-app.key(private key)go-private-app.key.pub(public key)
Library configuration
Now go to the library’s GitHub repository settings and add the content of the public key to the “Deploy Keys”.
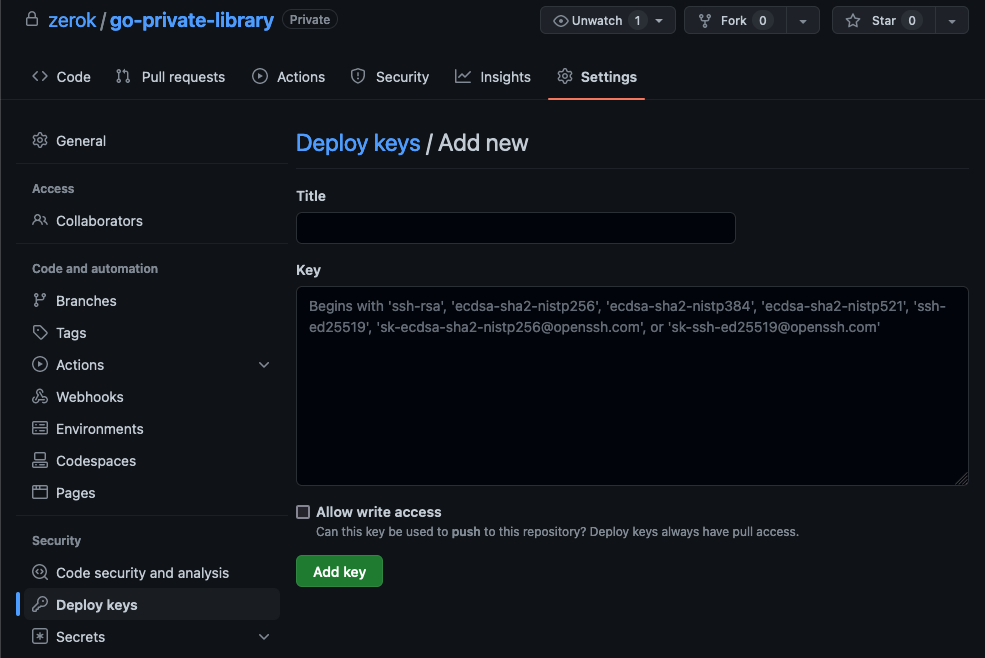
Application configuration
In the application repository, go to Settings » Security » Secrets » Actions and add the following two secrets:
SSH_PRIVATE_KEYwith the content of the private key fileKNOWN_HOSTSwith the host key of github.com
For reference, this would be the host key for github.com at the time of writing this:
github.com,207.97.227.239 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAq2A7hRGmdnm9tUDbO9IDSwBK6TbQa+PXYPCPy6rbTrTtw7PHkccKrpp0yVhp5HdEIcKr6pLlVDBfOLX9QUsyCOV0wzfjIJNlGEYsdlLJizHhbn2mUjvSAHQqZETYP81eFzLQNnPHt4EVVUh7VfDESU84KezmD5QlWpXLmvU31/yMf+Se8xhHTvKSCZIFImWwoG6mbUoWf9nzpIoaSjB+weqqUUmpaaasXVal72J+UX2B+2RPW3RcT0eOzQgqlJL3RKrTJvdsjE3JEAvGq3lGHSZXy28G3skua2SmVi/w4yCE6gbODqnTWlg7+wC604ydGXA8VJiS5ap43JXiUFFAaQ==
As a final step, add the SSH key to the CI pipeline in a step before build:
# ...
steps:
# ...
# Add the private key that is also enabled on the library repository:
- name: Install SSH key
uses: shimataro/ssh-key-action@v2
with:
known_hosts: ${{ secrets.KNOWN_HOSTS }}
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
# ...
Full workflow
Everything is in place now! The full workflow should look somehow like this:
name: Go
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Prevent the gotool from looking up the private repositories on the sum
# server.
env:
GONOSUMDB: "*github.com/zerok/go-private-*"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
# Now enforce that GitHub dependencies are fetched via SSH
- name: Enforce SSH
run: |
echo "[url \"ssh://git@github.com/\"]" > ~/.gitconfig
echo " insteadOf = https://github.com/" >> ~/.gitconfig
# Add the private key that is also enabled on the library repository:
- name: Install SSH key
uses: shimataro/ssh-key-action@v2
with:
known_hosts: ${{ secrets.KNOWN_HOSTS }}
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
- name: Set up Go
uses: actions/setup-go@v3
with:
go-version: 1.19
- name: Build
run: go build -v ./...
- name: Test
run: go test -v ./...

Do you want to give me feedback about this article in private? Please send it to comments@zerokspot.com.
Alternatively, this website also supports Webmentions. If you write a post on a blog that supports this technique, I should get notified about your link 🙂